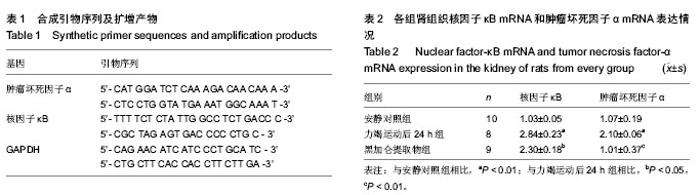
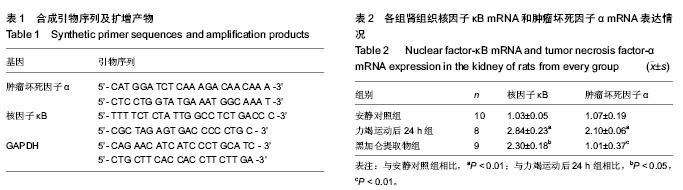
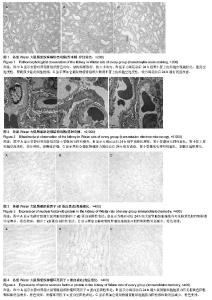
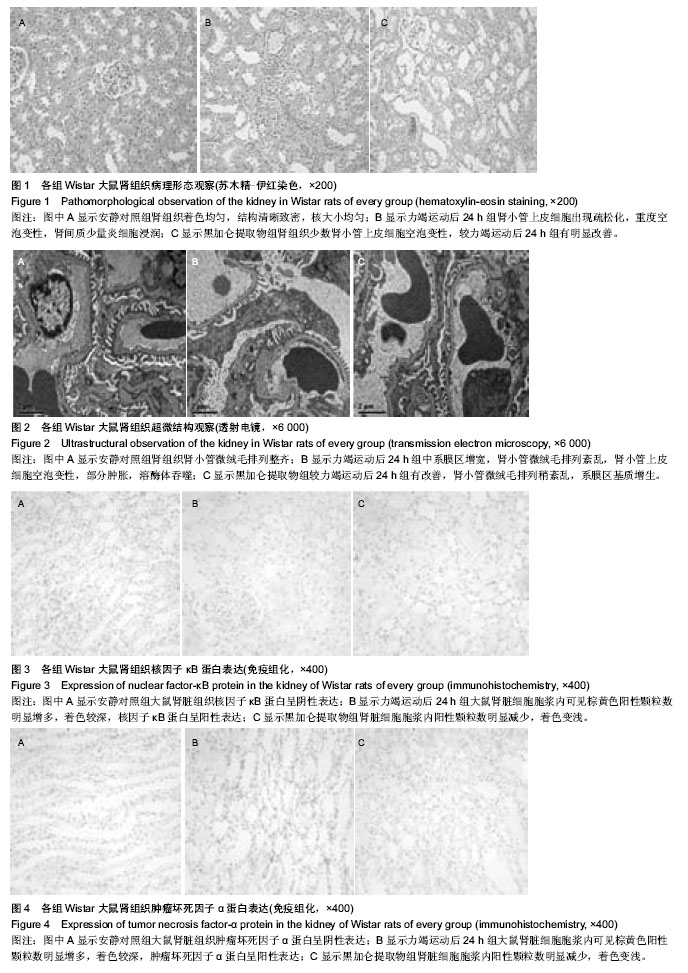
| [1] 黄旭东,吴广礼.一种新的过度运动致肾损伤模型的建立[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2011, 12(7): 593-596.
[2] Wu GL, Chen YS, Huang XD,et al.Exhaustive swimming exercise related kidney injury in rats - protective effects of acetylbritannilactone.Int J Sports Med. 2012;33(1):1-7.
[3] 扈诗兴.运动对肾脏形态结构和功能影响的研究进展[J]. 四川体育科学, 2009, 12(4): 31-34, 38.
[4] Bishayee A, Mbimba T, Thoppil RJ,et al.Anthocyanin-rich black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) extract affords chemoprevention against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis in rats.J Nutr Biochem. 2011; 22(11):1035-1046.
[5] Szachowicz-Petelska B, Dobrzyńska I, Skrzydlewska E,et al.Protective effect of blackcurrant on liver cell membrane of rats intoxicated with ethanol.J Membr Biol. 2012;245(4):191- 200.
[6] Nour V, Stampar F, Veberic R,et al.Anthocyanins profile, total phenolics and antioxidant activity of black currant ethanolic extracts as influenced by genotype and ethanol concentration. Food Chem. 2013;141(2):961-966.
[7] Edirisinghe I, Banaszewski K, Cappozzo J, et al. Effect of black currant anthocyanins on the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in vitro in human endothelial cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(16):8616-8624.
[8] 顾亚静, 赵效国,李莉,等.黑加仑提取物抗疲劳作用与GAT-2、Scd-2基因的关系[J].毒理学杂志, 2010, 24(2):119-122.
[9] 李莉,赵效国,马龙,等.黑加仑提取物抗疲劳作用的动物实验研究[J].营养学报,2008,30(5): 499-501.
[10] 宋燕华,严峻,夏勇,等.黑加仑提取物的致突变性和亚急性毒性研究[J].浙江预防医学, 2009, 21(3): 1-3,15.
[11] 郑云燕,蔡德雷,严峻,等.黑加仑提取物对SD大鼠致畸作用的研究[J].浙江预防医学,2010,22(12):20-23.
[12] Desjardins J, Tanabe S, Bergeron C,et al.Anthocyanin-rich black currant extract and cyanidin-3-O-glucoside have cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties.J Med Food. 2012;15(12):1045-1050.
[13] 肖辉,张月明,冷爱枝,等.黑加仑提取物抑制肿瘤生长及其机制的研究[J].毒理学杂志, 2007, 21(2):132-134
[14] Thoppil RJ, Bhatia D, Barnes KF,et al.Black currant anthocyanins abrogate oxidative stress through Nrf2- mediated antioxidant mechanisms in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012; 12(9):1244-1257.
[15] 赵君操,刘瑞雪,罗彬.黑加仑提取物抗疲劳作用的动物实验研究[J].河南医学研究, 2011,20(2): 131-133.
[16] Thomas DP, Marshall KI.Effects of repeated exhaustive exercise on myocardial subcellular membrane structures.Int J Sports Med. 1988;9(4):257-260.
[17] 张琳,熊正英,郝选明,等.白藜芦醇对大强度运动大鼠肾脏功能的保护作用[J].天津体育学院学报, 2011, 26(3): 208-210.
[18] 何芳.姬松茸多糖对运动力竭小鼠肾脏的保护作用研究[J].海军医学杂志,2013,34(3):155-157.
[19] 黄旭东,吴广礼.一种新的过度运动致肾损伤模型的建立[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2011,12(7):593-596.
[20] Goebeler M, Gillitzer R, Kilian K,et al.Multiple signaling pathways regulate NF-kappaB-dependent transcription of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene in primary endothelial cells.Blood. 2001;97(1):46-55.
[21] Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB.Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer.J Clin Invest. 2001;107(2):135-142.
[22] Chung KC, Park JH, Kim CH,et al.Novel biphasic effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on neuronal cell viability is mediated by the differential regulation of intracellular zinc and copper ion levels, NF-kappaB, and MAP kinases.J Neurosci Res. 2000;59(1):117-125.
[23] Lentsch AB, Ward PA.The NFkappaBb/IkappaB system in acute inflammation.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000; 48(2):59-63.
[24] 王建春,姜鹏,谢艳萍,等.急性肺损伤大鼠肺组织NF-κB表达的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2006, 16(16): 2448-2452.
[25] 杨季云,张思仲,郭红,等. 肿瘤坏死因子α通过激活NF-κB信号通路加快肝细胞周期进程[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2007, 34(6): 604-610.
[26] Lyall KA, Hurst SM, Cooney J,et al.Short-term blackcurrant extract consumption modulates exercise-induced oxidative stress and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009; 297(1):R70-81. |